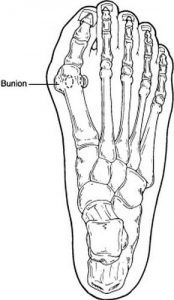
What is a Bunion?
A bunion is a bump on the joint at the base of big toe, known as first metatarsophalangeal joint (1st MPJ), that occurs when the bone or tissue at the big toe joint moves out of place. The visible bump actually reflects changes in the bony framework of the front part of the foot. A bunion is a progressive disorder. They begin with a leaning of the big toe, gradually changing the angle of the bones over the years and slowly producing the characteristic bump, which continues to become increasingly prominent. Usually the symptoms of bunions appear at later stages, although some people never have symptoms.
Causes
It is still not clear what exactly causes bunion deformity but possible causes are:
- Genetic (family history): If other members of your family have bunions, you have a higher risk of developing bunion but it does not mean you will definitely develop.
- Biomechanics of your feet: Abnormal function of joints in your feet can predispose to the development of bunion deformity.
- Arthritis: Rheumatoid arthritis, gouty arthritis or psoriatic arthritis.
- Other conditions or syndromes: Cerebral palsy and Marfan’s syndrome when ligaments are genetically loose. Poorly fitting shoes, pointy or narrow shoes, high heeled shoes.
Symptoms
- Pain or soreness over the prominence or inside the joint.
- Inflammation and redness.
- A burning sensation.
- Possible numbness.
Diagnosis
- Clinical presentation and examination.
- Imaging — Usually X-ray is sufficient.
Treatments
Early treatments are aimed at easing the pain of bunions, but they won’t reverse the deformity itself. These include:
- Footwear modification: Wearing the right kind of shoes is important. Choose shoes with a wide toe box and avoid pointy shoes or high heels which may aggravate the condition.
- Padding: Pads over the painful bony area help minimise pain.
- Activity modifications.
- Medications: Oral nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen, may be recommended to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Injection therapy: Injections of corticosteroids may be useful in treating the inflamed bursa (fluid-filled sac located around a joint) sometimes seen with bunions.
- Orthotics: Custom made orthoses may help relieve pain associated with bunion or may prevent it from becoming worse rapidly.
If non-surgical treatments fail to relieve bunion pain, the permanent surgical solution for their bunion is recommended.
A variety of surgical procedures is available to treat bunions. The procedures are designed to remove the bump of bone, realign the bony structure of the foot, and correct soft tissue changes that may also have occurred.